What is Dynamic Headspace?

Dynamic Headspace (DHS) is an extraction technique used to concentrate analytes from a solid or liquid sample. The sample is heated and agitated in a sealed vial and the headspace above the sample is purged onto a solid sorbent tube. The solid sorbent tube is then thermally desorbed into the gas chromatograph. DHS is a non-equilibrium technique, as the analytes in the headspace are constantly swept onto the tube during extraction. The lack of a stationary phase in this technique results in non-discriminatory collection of analytes from the sample. Low levels of detection can be achieved as exhaustive extraction conditions can be developed.
Download the DHS Infographic
Why GERSTEL Dynamic Headspace?
The GERSTEL DHS option automates the entire DHS process including thermostating, agitation, purging, drying and thermal desorption of the sorbent tube.
- Exhaustive purge of the sample headspace results in lower detection limits than static headspace, SPME and other widely used techniques
- Inert, unique valve free sample path provides no analyte discrimination and no cross contamination resulting in reliable and reproducible results
- Optimized system utilization through automated overlap of extraction and analysis steps with GERSTEL PrepAhead
- Highest flexibility with user defined extraction time, flow, temperature and absorbent
- Multiple water management options including trap material and temperature and automated dry purge
- Maestro software provides convenient and user-friendly operation. One method and one sequence table for complete extraction and GC analysis.
How does Dynamic Headpace Work?
The GERSTEL DHS uses standard 10 and 20 mL headspace vials for the sample. The sample vials are loaded into an appropriate tray on the MPS rail. The MPS moves the vial from the tray to the DHS agitator. The sample is incubated for a user defined time, temperature and speed. Once the sample has been agitated, the MPS moves the DHS carriage forward above the sample. A sorbent filled TD tube is transported to the carriage and inserted.
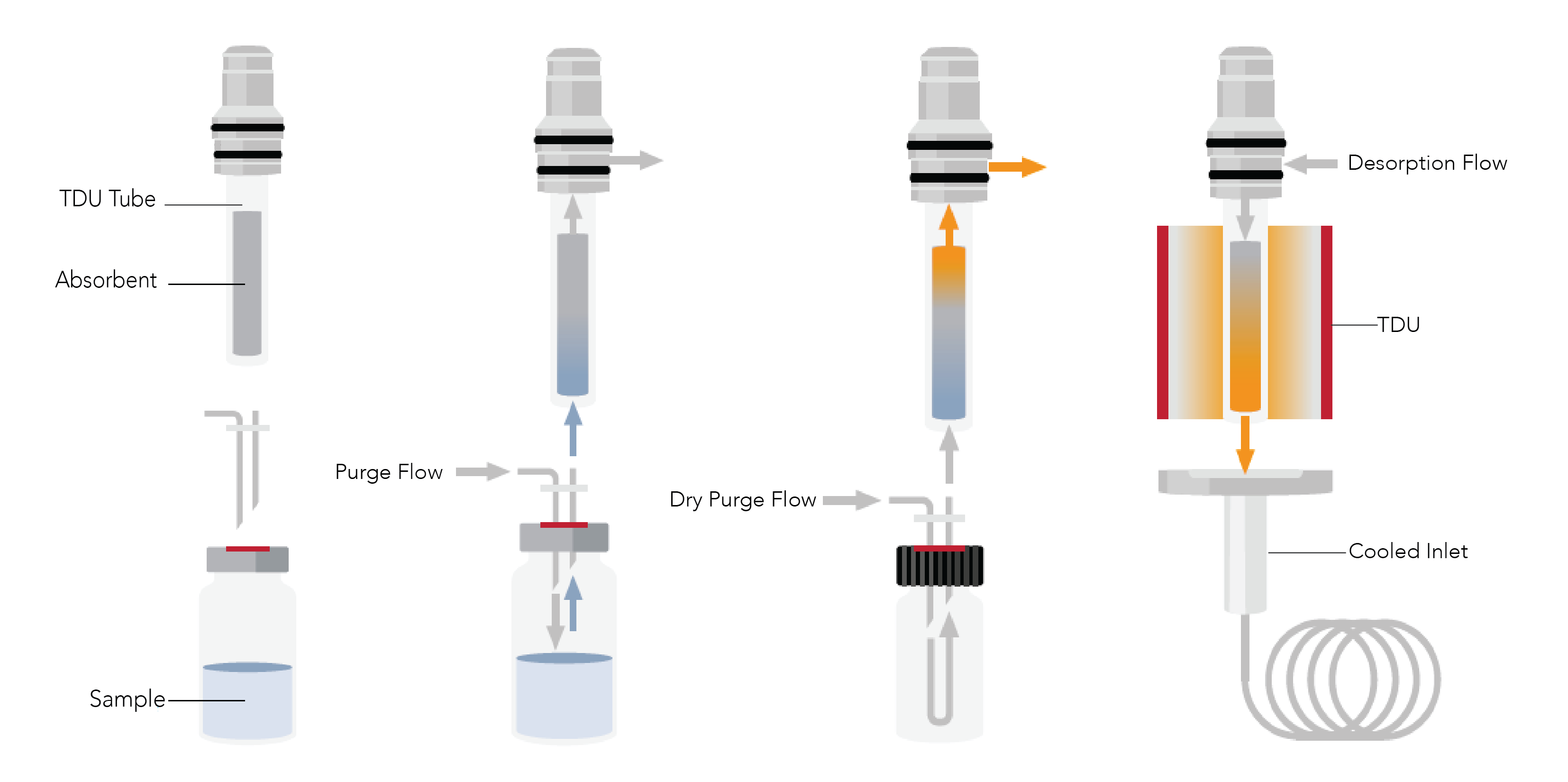
(Graphic shows the four stages of DHS: Preparation, Extraction, Dry Purge, Introduction)
Dynamic headspace can be used for a wide volatility range of compounds. For very volatile analytes, the total extraction volume is usually small and a multibed adsorbent is used. For volatile compounds, a larger sample volume is used and a single bed adsorbent, like Tenax-TA®, can be used. For non-volatile, hydrophilic compounds, a full evaporation technique (1) can be applied. In this technique, a small amount of sample is evaporated and swept onto the sorbent tube. These methods can be combined for a comprehensive analysis of the sample, where required.
What is Dynamic Headspace used for?
The GERSTEL Maestro software also allows sample preparation along with DHS analysis. The MPS can be set up to automatically add an internal standard or derivatization agent to a sample. The MPS can also be set up to prep calibration standards.
The GERSTEL MPS with DHS option is highly flexible. The DHS Large option can be added onto the standard DHS and allows for the use of larger vessels. The vessel sizes include 250, 500 and 1,000 mL. They can accommodate larger sample sizes without the need to cut or otherwise manipulate a sample to get it into a standard headspace vial. The Maestro DHS software dialog allows the content of the vial to be prepurged, if desired, prior to analysis. The prepurge can be used to eliminate room air from the sample or blanket the sample with an inert gas prior to analysis. The sample contents can be prepurged through an empty TD tube or trapped on a separate sorbent filled tube. The DHS Large option is a single position device. If automation of multiple large vessels is desired, the GERSTEL DHS-L autosampler can be used to automate the analysis of up to 11 samples. These vessels can be set up as small microchambers for materials emission experiments.
The GERSTEL Maestro software also has an option called “DHS No TDU”. This option allows DHS extraction of a sample without direct analysis of the sample. The TD tube is placed back in the TD tray. This can be useful for continuous monitoring of off-gassing from a sample and off-line preparation of a sample for thermal desorption on another instrument, like a TD-GC-MS-TOF. This option can also be used for multiple preparations of the same sample. The TD tubes can then be desorbed into the same GC run using the Maestro TDx multidesorb mode, where multiple tubes are desorbed and the analytes are stacked in the GERSTEL CIS inlet. This mode results in the most mass on-column and can be very important in determining analytes, such as off-odors, at very trace levels.
Dynamic headspace is applicable to a wide range of markets including food, flavor, fragrance, beverage, chemicals, forensics, materials emission and environmental. Anywhere trace analysis is needed.
- Marlelov, J.P Guzowski, Jr., Analytica Chimica Acta, 276 (1993) 235-245.
Download the infographic here

